真空蒸发镀膜Vacuum evaporation coating
在高真空中用加热蒸发的方法使镀料转化为气相,然后凝聚在基体表面的方法称蒸发镀膜(简称蒸镀)。和液体一样,固体在任何温度下也或多或少地汽化(升华),形成该物质的蒸气。
The method of heat evaporation in high vacuum to convert the plating into gas phase and then condense on the surface of the matrix is called evaporation coating (abbreviated as evaporation). Like liquids, solids more or less vaporize (sublimate) at any temperature, forming the vapor of the substance.
在高真空中,将镀料加热到高温,相应温度下的饱和蒸气向上散发,蒸发原子在各个方向的通量并不相等。基片设在蒸气源的上方阻挡蒸气流,蒸气则在其上形成凝固膜。为了弥补凝固的蒸气,蒸发源要以一定的比例供给蒸气。
In a high vacuum, the plating is heated to a high temperature, and the saturated vapor at the corresponding temperature is emitted upwards. The fluxes of the evaporated atoms in all directions are not equal. The substrate is positioned above the vapor source to block the vapor flow, on which the vapor forms a solidified film. In order to make up for the solidified vapor, the evaporation source must supply the vapor in a certain proportion.
蒸镀的加热方法有电阻加热蒸镀和电子束加热蒸镀。利用电子束加热可以使钨(熔点3 380 ℃)、钼(熔点2 610 ℃)和钽(熔点3 100 ℃)等高熔点金属熔化。图6-11 为电子束加热蒸发源示意图。
The heating methods include resistance heating and electron beam heating. Electron beam heating is used to melt metals with high melting points such as tungsten (melting point 3 380 ℃), molybdenum (melting point 2 610 ℃) and tantalum (melting point 3 100 ℃). FIG. 6-11 is a schematic diagram of the electron beam heating evaporation source.
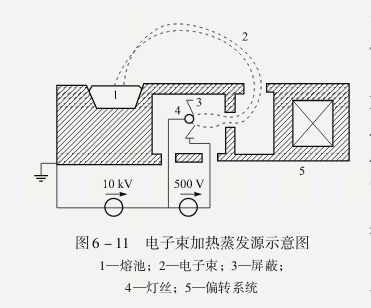
蒸镀既可以进行纯金属的镀制,也可进行合金膜的镀制和化合物膜的镀制。在进行合金膜的蒸镀时,要求在整个基片表面和膜层厚度范围内都必须得到均匀的合金组分。为达到此要求一般有两种基本方式:单电子束蒸发源沉积和多电子束蒸发源沉积(如图6-12 所示)。
Evaporation can be used for the plating of pure metal, alloy film and compound film. During the evaporation of the alloy film, uniform alloy composition must be obtained in the whole substrate surface and the thickness of the film. There are generally two basic ways to achieve this requirement: single electron beam evaporation source deposition and multi-electron beam evaporation source deposition (as shown in figure 6-12).

多电子束蒸发源是由隔开的几个坩埚组成,坩埚数量按合金元素的多少来确定,蒸发后几种组元同时凝聚成膜。单电子束蒸发源沉积合金时会遇到分馏问题:以 Ni、Cr二元合金为例,它经常用于制造电阻薄膜和抗蚀层。蒸镀的合金膜,其组成为 80 / 20。蒸发温度约 2 000 K,而铬在2 000 K时的蒸气压强比镍要高 100 倍。如果镀料是一次加热,则因铬原子消耗较快,而使镀层逐渐贫铬。解决分馏问题的办法是连续加料,熔池的温度和体积保持恒定是这种镀膜工艺成功的关键。如果合金组元蒸气压差别过大,沉积合金的工艺便受到限制。
The evaporation source of multi-electron beam is composed of several separated crucible, and the number of crucible is determined according to the number of alloy elements. Fractionation problems occur when alloys are deposited by single electron beam evaporation sources: Ni and Cr binary alloys, for example, are often used to make resistive thin films and corrosion resistant layers. A evaporated alloy film consisting of 80/20. The evaporation temperature is about 2, 000 K, and the vapor pressure of chromium at 2, 000 K is 100 times higher than that of nickel. If the plating is a heat, because of the chromium atom consumption faster, so that the coating gradually lean chromium. The solution to the fractionation problem is continuous feeding, and keeping the temperature and volume of the molten pool constant is the key to the success of this coating process. If the vapor pressure of the alloy components is too different, the process of depositing the alloy will be limited.
大多数的化合物在热蒸发时会全部或部分分解,所以用简单的蒸镀技术无法由化合物镀料镀制出相同化学比的膜层。但有一些化合物,如氯化物、硫化物和硒化物,甚至少数氧化物如B2O3、SnO可以采用蒸镀。因为它们很少分解或者当其凝聚时各种组元又重新化合。然而不仅有热分解问题,也有与坩埚材料反应从而改变膜层成分的问题,这些都是化合物蒸镀的限制因素。镀制化合物的另一途径是采用反应镀,例如镀制 TiC 是在蒸镀 Ti 的同时,向真空室通人乙炔气,于是基片上发生以下反应而得到 TiC 膜层:2Ti 斗 C2H2→2TiC+H2。
Most compounds decompose in whole or in part during thermal evaporation, so it is impossible to produce films with the same chemical ratio by simple evaporation technology. However, some compounds, such as chloride, sulfide and selenide, and even a few oxides, such as B2O3 and SnO, can be evaporated. Because they rarely break down or recombine when they condense. However, there are not only thermal decomposition problems, but also the reaction with crucible materials to change the composition of the film, which are the limiting factors of compound evaporation. Another way of plating the compound is to use reactive plating. For example, TiC plating is to transfer acetylene gas to the vacuum chamber at the same time of Ti evaporation, so the following reaction occurs on the substrate to obtain TiC film :2Ti C2H2→2TiC+H2.
真空蒸镀只用于镀制对结合强度要求不高的某些功能膜。例如用作电极的导电膜、光学镜头用的增透膜等。蒸镀用于镀制合金膜时,在保证合金成分这点上,要比溅射困难得多,但在镀制纯金属时,蒸镀可以表现出镀膜速率快的优势。蒸镀纯金属膜中,90%是铝膜。
Vacuum evaporation is only used for plating some functional films that do not require high bonding strength. For example, conductive film used as electrode, antireflection film used in optical lens, etc. It is much more difficult to guarantee the alloy composition than sputtering when it is used for the plating of alloy films, but when it is used for the plating of pure metal, it can show the advantage of fast coating rate. Among the evaporated pure metal film, 90% is aluminum film.
来源:《模具材料与表面处理》主编 康俊远 副主编 李立明 徐勇军.—北京理工大学出版社,2007.6
